Mud losses reasons
• Lowering the pipes very quickly leads to the formation of additional pressure on the layer.
• The formation of a mud envelope around the bit (BIT) and the gathering of rock pieces around the pipes leads to closing or minimizing the annular space between the walls and the pipes, as when the mud is to be recycled, its pressure is high, which leads to breaking the weak layer.
• Starting to rotate the mud in a large amount after the withdrawal and downloading operations, as the mud was static and thus has a high gelatinous strength. Therefore, this large amount pushed quickly will meet resistance that leads to the formation of opposite pressure on the layer that may cause it to break.
• An increase in the viscosity of the mud and the strength of the gelatinousness during drilling operations leads to the operation of the pumps at high pressure, which causes the breakage of the weak layer.
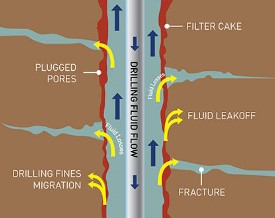
For the purpose of overcoming the appearance of gas or water flow, the density of the mud increases, or a choke may be used, which leads to the formation of additional pressure on the layer causing its fracture.
• An increase in the density of mud due to the ineffectiveness of the purifiers on the surface.